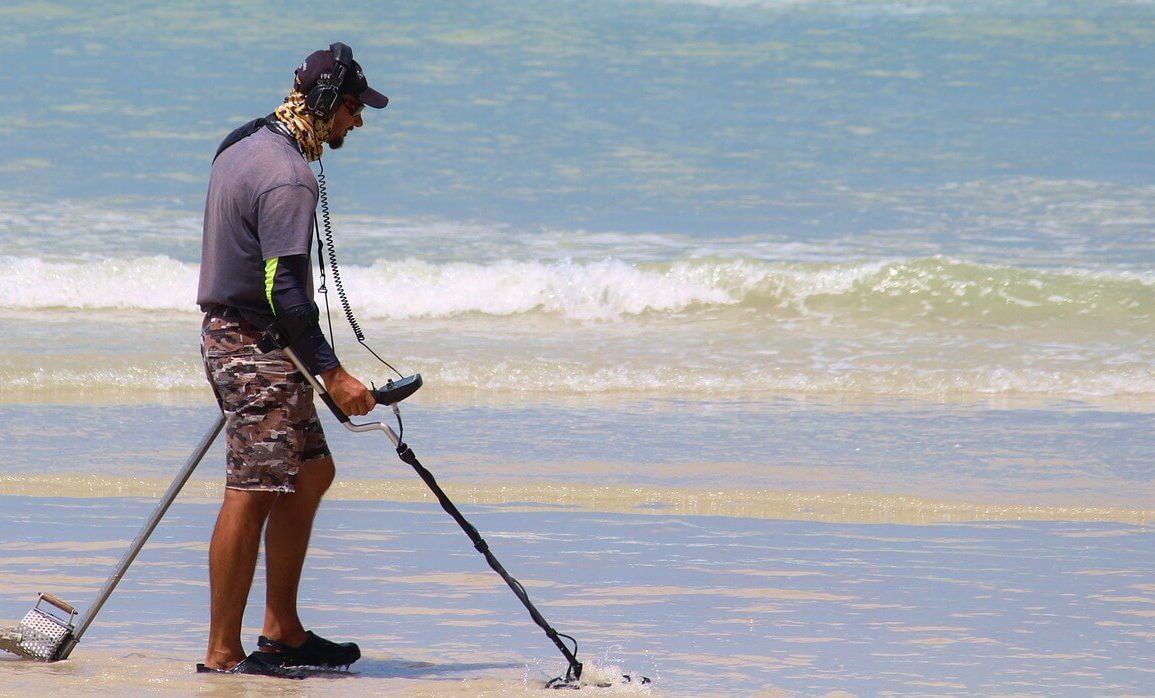
Are you interested in metal detectors? Do you want a new hobby that lets you discover tons of metals? If so, you need to get familiar with a metal detector and how it works.
Using a metal detector gives you a chance to discover different metals, such as gold, tungsten, titanium, platinum, bronze, and brass. The most in-demand are gold detectors since gold is in the top 3 most valuable metals.
Metal detecting requires a lot of patience, and you also need to accept that sometimes you will go home with nothing. However, your patience is worth it once you find interesting objects.
If you want to know more about metal detectors, continue reading!
What is a Metal Detector?
A metal detector refers to a handheld device designed for detecting metal objects on the ground surface or those buried underground. Modern metal detectors can detect all kinds of alloys and metals. There are also specialized metal detectors that can detect metals underground, approximately one meter deep.
This device works by sending an electromagnetic field coming from the search coil into the ground. A metal object or target inside that electromagnetic field becomes energized and then retransmits the electromagnetic field on its own. Once the search coil of the device receives the retransmitted field, the device alerts the user with a target response.
How Does A Metal Detector Distinguish Between Metals
A metal detector is built with a discrimination dial, which signals the device only to detect specific metals and ignore other objects.
To give you a bigger picture of how the device distinguishes metals, check out the following:
Differentiate with Discrimination
Discrimination is the most common method to differentiate metals. Each metal type produces a varying response once subjected to AC. The equipment understands which metal is in question by recording the phase response.
The user can program the device so that it only responds to a specific metal type and others. This differentiation technique is to be implemented. All you have to do is set the device to observe or ignore a particular phase response.
Differentiate Using A Screen Indicator
A metal detector comes with a screen indicator. Every metal type is assigned as a particular target ID. Once this target ID is found, it is displayed on the screen.
On the other hand, it is standardized and varies across manufacturers and countries. The good news is that each manufacturer provides a guide that explains the target ID within the documentation.
Differentiate with Tones
If you are on the go, the tones are a very noticeable differentiation technique. Historically, metal detectors only have one tone. Modern detectors are built with at least two tones. A “good” tone is dedicated to desirable metals, and a “bad” tone is intended for the trash.
Other latest detectors with more than two tones form various distinct audio combinations for various metals. The tone’s strength gives the user an idea of how deep a metal is buried.
Different Key Detecting Concepts
A metal detector comes with various key detecting concepts, including:
Frequency
The detectors’ frequency is a critical characteristic that helps identify how well targets are detected. A single frequency detector that transmits at a high frequency tends to be more sensitive to small targets. A single frequency detector that transmits at a low frequency provides more depth on large targets.
Ground Balance
Ground balance refers to the variable setting that helps increase the detection depth in the ground. The minerals like salt are found in the ground, such as in fine iron particles or wet beaches, respond to the metal detector’s magnetic field the same as the target does.
Since the ground has a much larger mass than the buried target, the mineralization’s effect can easily mask the small targets. The ground balance setting eliminated the response ground signals to correct that scenario. In return, the user hears the target signal clearly while staying away from ground noise.
Different Depth Factors
For sure, you also want to know how deep a metal detector would go. The device can go as the coil diameter. In other words, the larger the coil, the deeper the device detects.
On the other hand, the detection depth also depends on different environmental factors and detector technology. Below are the various depth factors you should know before you start your hobby of metal detecting:
- Target Size. A larger target detects deeper compared to a smaller target.
- Target Orientation. A horizontal coin that lies flat is detected deeper compared to a vertical coin on edge.
- Target Shape. A circular shape like rings and coins is detected deeper compared to a long thin shape like necklace and nails.
- Target Material. A high conductive metal like silver is detected deeper compared to a low conductive metal such as gold or lead.
Does A Metal Detector Work in the Rain?
A metal detector works well even in the rain. Why? Because rain helps increase the soil’s conductivity. Then, the detector becomes more sensitive and detects metals at greater depths. Don’t worry; rain will not damage your waterproof metal detector.
Conclusion
Do not let your vacant time leave you unproductive. You can try a new hobby like metal detecting.
Hopefully, the ideas above give you a better understanding of metal detectors and how they distinguish between metals. This hobby might be overwhelming at first, but you will enjoy the experience later on. Plus, you can invite your loved ones to visit different places and hunt for interesting treasures.